Ever wonder how your favorite local farm stand manages to have so much variety for such a long period of time? Farmers use succession planting to maximize their harvests and provide a wide variety of vegetables for a long season.
Succession planting is when you stagger plantings or plant multiple crops in the same area throughout the season. Each time a crop is finished you pull it and plant a new one. This allows commercial growers to reap large, continued harvests.
It’s not just for farmers though! Succession planting is super easy and great for backyard gardeners too. With a little extra planning you can get more production for your existing garden space.
Getting Started
Choosing Varieties
Almost any crop can be succession planted but different crops are succession planted for different reasons and offer different results.
Plants like corn, broccoli, and cabbage are often planted in successions to achieve more than just a single harvest. Many people also choose to plant successions of summer squash and cucumbers as just a few plants can produce a massive amount at their height of production.
Radishes, swiss chard, green onions, and carrots are great for planting multiple successions or sneaking in between plantings of other crops. They’re quick to grow and favored by urban gardeners and farmers.
Cool season crops are also good choices as they can be planted in the early spring or fall when hot weather crops won’t be taking up space in your garden.
Additionally you can select multiple varieties of crops with different harvest times. For example Golden Acre Cabbage takes just 62 days to harvest while Premium Late Flat Dutch is 100 days to harvest. Plant a little of both at the same time for different harvests.
Check out this post by Ira Wallace for more awesome ideas!
Planning
Succession planting is most successful when you have a good solid plan. To start you’ll need to know which crops you want to grow, their days to harvest, and the length of your growing season. Here at Southern Exposure we’re in zone 7 and have roughly 180 frost free days, plenty of time to get multiple successions of many crops.
Once you have these details you can start organizing your plantings. You’ll want your garden layout and a calendar or datebook. Alternatively you can try out the Southern Exposure Garden Planner.
Using your knowledge and tools you can judge the general times specific crops will be harvested and which one can be grown next in their place. To help avoid disease, pest, and nutrient issues avoid replanting the same crop in the same space.
If you’re not interested in a written plan just remember each time crop is harvested a new crop is planted. On the Facebook page we’ll continue to have what to plant this week guides which can help you decide which crops you should replant throughout the summer.
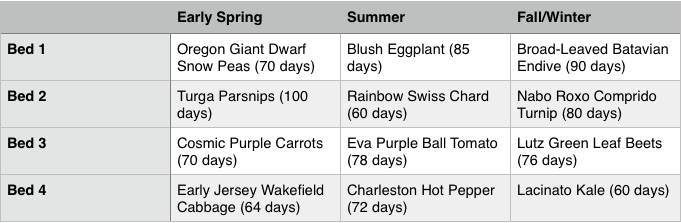
Example Combinations for Zone 7A
Staggered Planting
Succession planting can be tough especially if you’re someone who has huge springtime garden dreams but gets so busy by midsummer you barely remember where you planted the what let alone find time to harvest. Surprisingly succession planting can also help you keep your garden manageable.
One of the easiest ways to start succession planting is simply to not plant an entire crop all at once. For example if you want to have a bunch of sweetcorn throughout the summer rather than a single harvest simply plant a few rows every two weeks. This method is great for people who want to enjoy fresh produce but don’t necessarily have time to put up a large harvest. Of course you’ll need to be aware of your days to harvest and first frost date ensuring you give all your crops enough time to fully mature.
Cool Season Crops
Cool season crops are another great option especially for those with hot summers. Many plants like turnips, pak choi, arugula, and lettuce that prefer cool whether can be sown early in the spring and again in the late summer or early fall in order to reap a second harvest. In the summer, heat loving crops can take their place in the garden.
It sounds awesome but sowing crops late in the season in order to get a fall harvest can be tricky. For fall crops it’s important to keep the soil as cool and moist as possible if your planting in the heat of summer. Check out Tips for Sowing in Hot Weather by Lisa Dermer & Ira Wallace for more information.
You can also extend these crops’ season even further through the use of cold frames , hoop houses, and row covers.
Fertility
It’s important to note that growing more crops in the same space throughtout the season will use more nutrients. You’ll need to be careful not o over-tax your garden. Consider the use of crop rotation, cover crops, compost amendments, and homemade liquid fertilizers to meet your plants nutrient requirements.
All of these are fairly easy to achieve at home and can make your garden more productive while saving you money on pricey store bought garden amendments.
No matter why you got into gardening succession planting can help you turn things up a notch. You can use it to have less overwhelming harvests, enjoy more of your family’s favorite vegetables, grow more food, and even extend your growing season.
What’s your favorite crop for succession planting? Tell us in the comments!



 Lisa Dermer & Ira Wallace
Lisa Dermer & Ira Wallace 4. Sow successions! Two weeks after your first sowing make another planting of the same varieties or other, earlier-maturing types.
4. Sow successions! Two weeks after your first sowing make another planting of the same varieties or other, earlier-maturing types.
