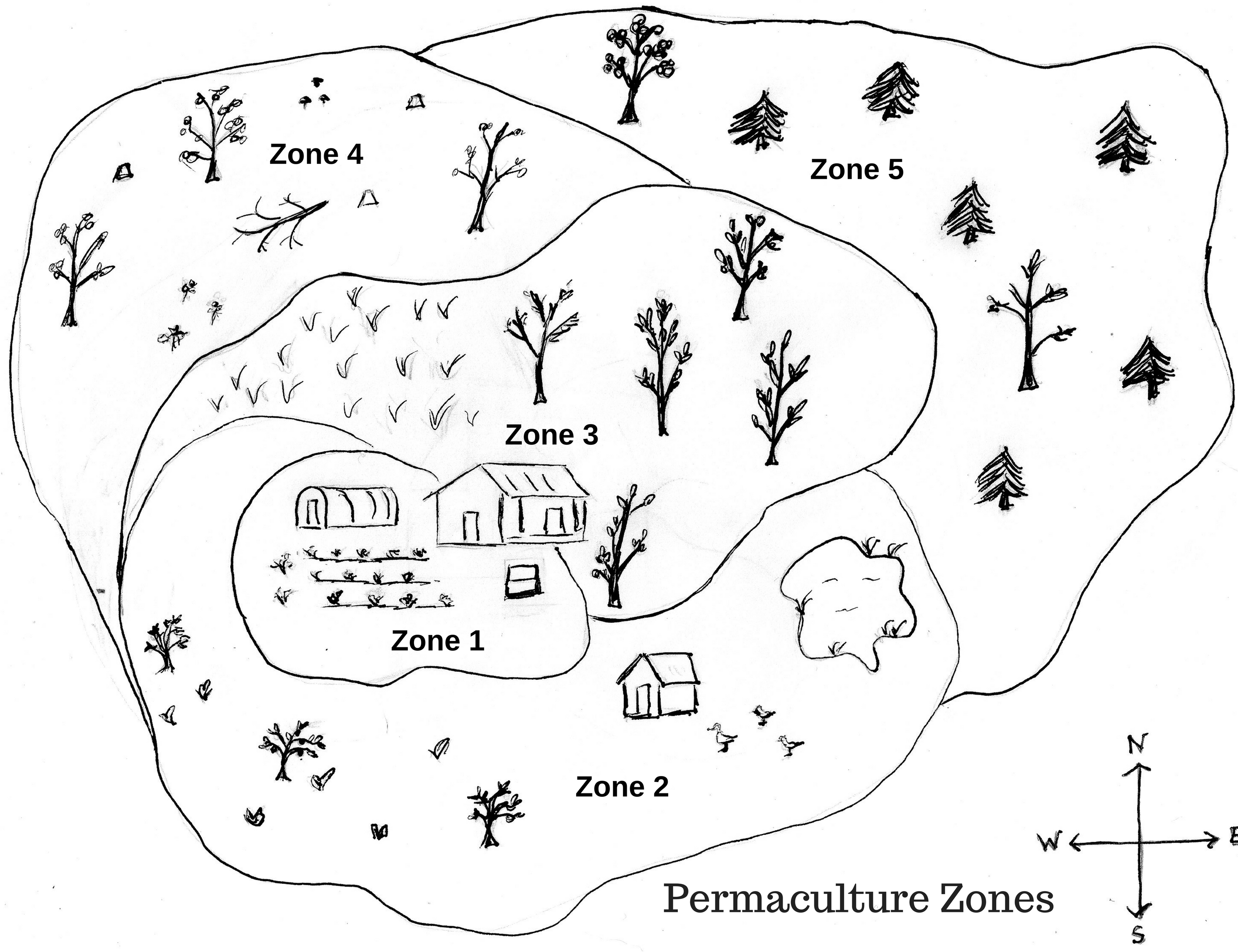
Many permaculture enthusiasts choose to design their garden and property based on a zone system. The premise of this system is to layout your property in as efficiently as possible. Using this method to plan ahead can help ensure your property is easily accessible and productive. Even if you live on a tiny, already established property you can still utilize permaculture zones to help organize your garden or farm.
Typically there are 6 different zones with zone 0 being the home. While there is certainly variations based on personal needs and property characteristics often zones 1-5 go from outward from the house 1 being the closest and 5 being the farthest. Areas in a zone 1 require the most frequent care while zone 5 requires no maintenance.
Zone 1
Zone 1 is typically the closest to the home or areas you visit most frequently. For this reason features in zone 1 should be those that you use most frequently or need the most care. Good examples include small greenhouses or cold frames which house tender seedlings or have to be carefully monitored, culinary herb gardens, worm farms for processing kitchen scraps, etc.
In this example zone 1 is a small area around the southern side of the home containing a worm farm, small hoop house, and an herb and salad garden.
Zone 2
While it may not be accessed quite as frequently as zone 1, zone 2 is probably where you’ll grow the last majority of your food. Zone 2 areas typically include things like perennial plants, annual vegetable plantings, and food forests with a combination of plants, shrubs, and trees. Other items often located in a zone 2 include compost bins, chickens coops, beehives, ponds, and potting sheds.
In the example zone 2 has a food forest with smaller sized fruit trees, annual plants, and perrenials all intermingled. It also features a duck coop and small pond.
Zone 3
Zone 3 can still be productive agricultural land but needs less tending than zones 1 and 2. These areas may include livestock pastures, orchards of larger fruit and nut trees, and possibly large areas of staple crops.
In the example there’s and large fruit and nut orchard that partially extends around the southern side of the home to offer shade in the summer as well as a wheat field.
Zone 4
This area is a lightly managed piece of the property. It can be used for foraging, encouraging or growing woodland medicinals and mushrooms, harvesting timber or firewood, and even occasional grazing.
For this is example zone 4 is used to harvest wild mushrooms and firewood as well as cultivate a woodland medicinal herb patch.
Zone 5
This is your wilderness area. It’s typically left untouched and pristine for the benefit of wildlife, nature, and your enjoyment and recreation. For many zone 5 will be the farthest away from your home, a place to take relaxing walks but not necessarily visited as frequently as areas that require management. On the other hand some may choose to have a section of zone 5 extend right to their house to offer more frequent opportunities to observe and enjoy nature.
If you have a property of any size you can utilize some of the permaculture zones planning method. Breaking your property into sections can help ensure you create a space that’s productive, functional, beautiful, and good for wildlife.
Pin it for later.












