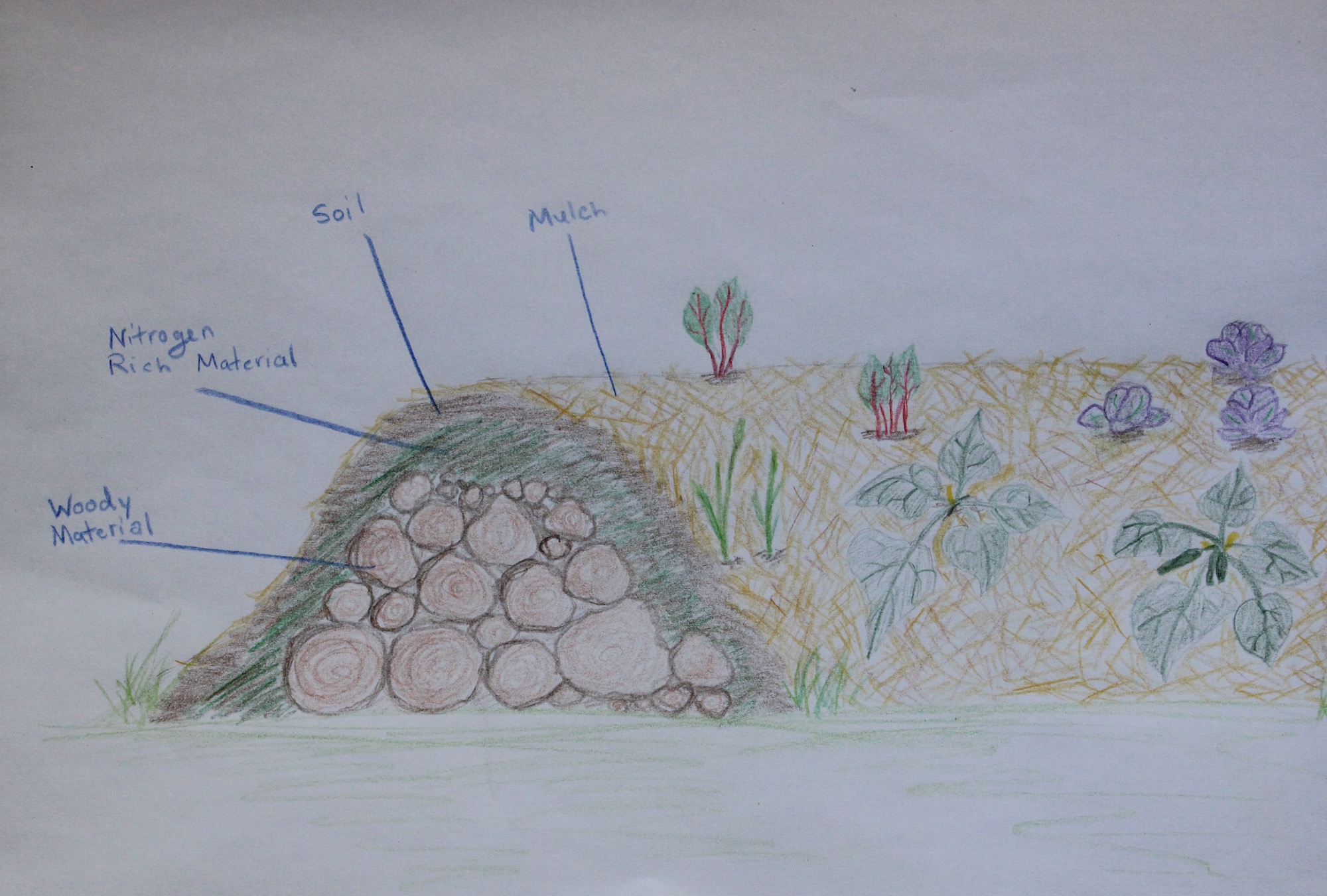
Odds are you’ve probably heard of permaculture but do you really understand what it is? Often thought of as merely gardening methods, permaculture actually reaches beyond techniques like hugelkultur beds and fruit tree guilds. Bill Mollison one of the founders of permaculture defined it as,
“The conscious design and maintenance of agriculturally productive systems which have the diversity, stability, and resilience of natural ecosystems. It is the harmonious integration of the landscape with people providing their food, energy, shelter and other material and non-material needs in a sustainable way.”
Permaculture may not be the perfect solution for everyone but its teachings certainly have value. A great way to get started with permaculture is to learn about the principles and ethics of permaculture and try to apply them to your garden.
Permaculture Principles
- Observe and interact
- Catch and store energy
- Obtain a yield
- Apply self regulation and accept feedback
- Use and value renewable resources
- Produce no waste
- Design from patterns to details
- Integrate rather than segregate
- Use slow and small solutions
- Use and value diversity
- Use edges and value the marginal
- Creatively use and respond to change
Permaculture Ethics
There are also three ethics: earth care, people care, and fair share. These ethics can be kept in mind when making decisions to create a sustainable garden.
Here are a few ways you can use permaculture principles and ethics in your garden.

Seed saving is a great way to take your gardening a step further. It increases your self-reliance and the resiliency of your garden. It allows you to play a role in preserving heirlooms and biodiversity for future generations.
When you save seeds you deepen your understanding of the natural world. You learn that beets are biennial, melon varieties have to isolated at least 1/8 mile for home use, and that garlic must be properly cured. You’ll get to know your plants better and appreciate your garden all the more.
If you’re nearby, SESE’s Ira Wallace will be at the Allegheny Mountain Institute hosting a seed saving workshop on July 3rd.
Compost
No matter where you live you can compost. If you live in an apartment you can look into vermicomposting or you might be able to join a community composting organization. If you have a yard you can set up your own compost bin. There are many easy DIY tutorials online.
Composting can significantly reduce the amount of waste headed for landfills and help add nutrients back to your garden. If you live rurally and are feeling extra adventurous you can try using a composting toilet which helps save water too!

Reduce Plastic
If you pay attention to environmental news or science you’re probably bombarded with the rather frightening statistics about plastic. Scientists have discovered micro-plastics in Arctic ice and according to National Geographic approximately 18 billion pounds of plastic ends up in the ocean every year!
You might be wondering what this has to do with gardening but somewhat surprisingly agriculture is now heavily dependent on disposable plastic. From seed trays to hoop-house covers and product packaging, it has become so prevalent there’s a name for it: plasticulture.
Growing food at home can help reduce food packaging especially if you opt to preserve you harvest in re-usable containers, canning jars, or silicone bags. Take it a step further and take plastic out of your garden too. Check out our post 7 Ways to Start Seeds Without Plastic, to learn about alternatives to plastic seed trays.
Create an Efficient Property
Using permaculture zones to design your property, even if you just have a small suburban backyard, can help you make the most of your space. Check out Property Planning with Permaculture Zones.
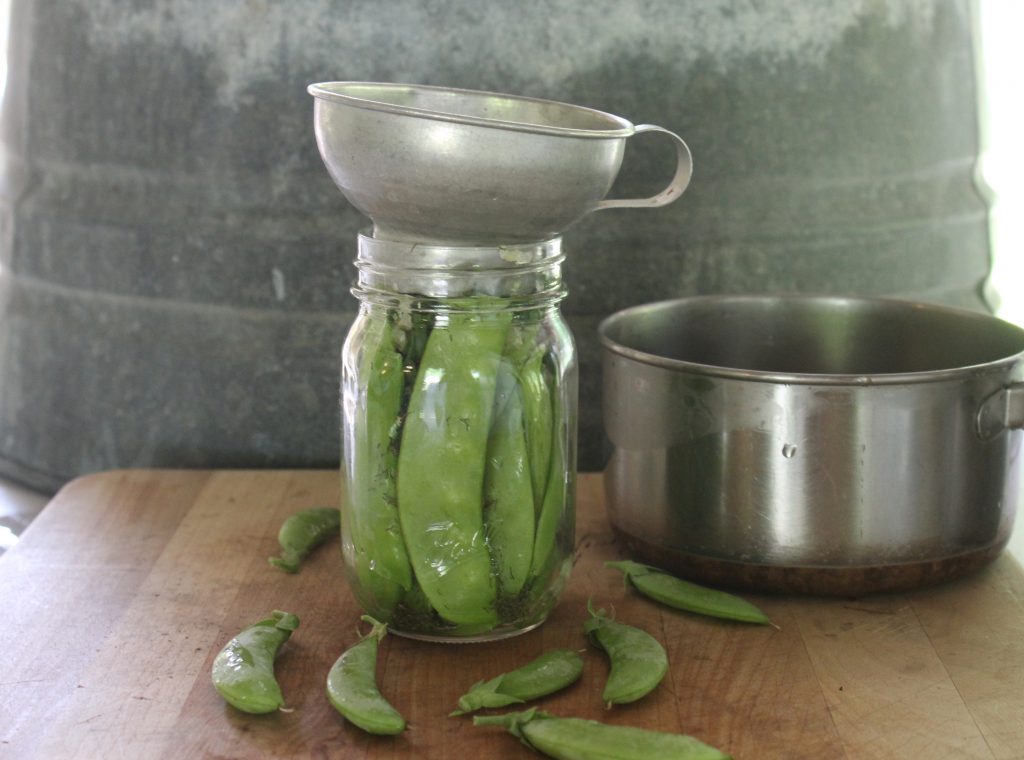

Feed Some Friends
Throw a garden party this summer! Share your harvest or get together for some harvesting, shelling, or canning. Put down your phones and connect with people. Sow the seeds (pun intended) of gardening and love for fresh meals in others.
Install a Rain Barrel
Catching and storing water improves your self-reliance and helps the environment. If you have a filter or are willing to install a rainwater system you can use rainwater for household use. Even if you just want to set up a simple DIY barrel you can use rainwater to water your garden.
Collecting and using this water prevents stormwater run-off that otherwise can lead to excessive nutrient loads in local watersheds. These nutrients can cause algae blooms, harmful to both human and marine life.
Be sure to check local regulations before installing a rain barrel.
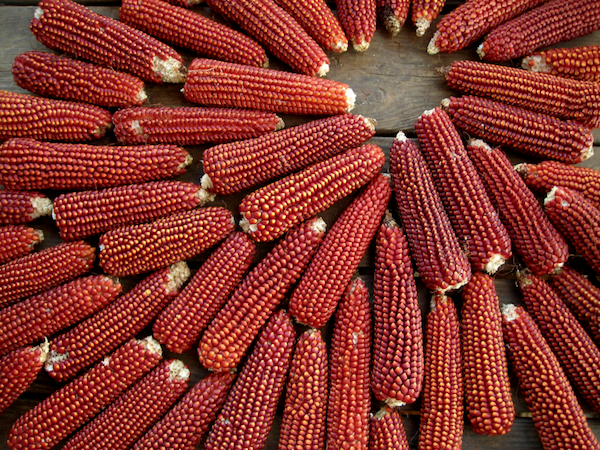

Even many small plots have room for a few storage crops like flour corn, dry beans, and sweet potatoes. Growing these simple foods can keep your pantry full and reduce your reliance on the grocery store. You’ll learn about the bounty your land can produce and how to create from scratch meals with staples. You’ll reduce your food miles, bills, and might get a little healthier too.
Teach Others
If you have the opportunity, pass on your skills. Get your children, grandchildren, or nephews and nieces involved in the garden. Share seeds and wisdom with a curious neighbor. Offer to teach a class at a community center or school. These moments will connect you with your community and inspire others.

Learn Something New
No one is too old or too good at gardening to learn something new. Consider signing up for a local gardening, preserving, or permaculture class. You can also watch a documentary or read a book. Facebook can wait!
Plant Perennials
Perennial crops like asparagus, rhubarb, berry bushes, and fruit and nut trees all require a larger up-front investment than annual plants. Almost all perennials require a least a year or two to get established (if not more) before you’ll see any harvest. They also frequently cost more to purchase. However, perennials are worth the wait.
Many will thrive in areas ill-suited for annual crops and help you achieve a larger harvest. Perennials are also an excellent way to diversify your crops and land use. Many like will also create habitat for local wildlife as well.
These simple steps can have a big impact. As you work on your garden consider the permaculture principles and ethics to live a more sustainable life closer to nature.